SSH 2
Configuring SSH :
- generate keys by command ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/example/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/home/example/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/example/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /home/example/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
5e:3f:6f:57:42:d0:b2:f5:aa:98:53:0f:20:5d:b0:2a example@example
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/example/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/home/example/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/example/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /home/example/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
5e:3f:6f:57:42:d0:b2:f5:aa:98:53:0f:20:5d:b0:2a example@example
it will generates 2 files in ~/.ssh (id_rsa and id_rsa.pub)
id_rsa : it's a private key ,should be protected.
id_rsa.pub : it's a public key .
- installing public key
- server trust client
1-server copy client's public key to ~/.ssh/ (ssh-copy-id or scp).
2-change public key name into authorized_keys.
3- change it's permission into 600 (chmod 600 authorized_keys).
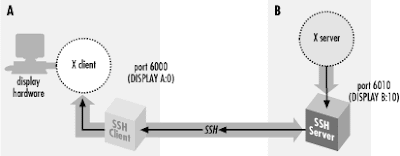
- x11 session forwarding
edit sshd_config : nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
and check these option :
X11Forwarding yes
X11DisplayOffset 10
X11UseLocalhost yes
Then connect to remote computer by command:
ssh -X username@server
Securing SSH :
- don't allow root log-in
edit sshd_config nano/etc/ssh/sshd_config , you will find #PermitRootLogin yes
remove # and change value into no PermitRootLogin no
- ByTCP Wrapper
Add SSHD to TCP Wrapper to allow and deny hosts to connect to SSHD
edit /etc/hosts.allow or /etc/hosts.deny
for exampleto deny host 192.168.0.132 to connect to SSH server
nano /etc/hosts.deny
sshd : 192.168.0.132